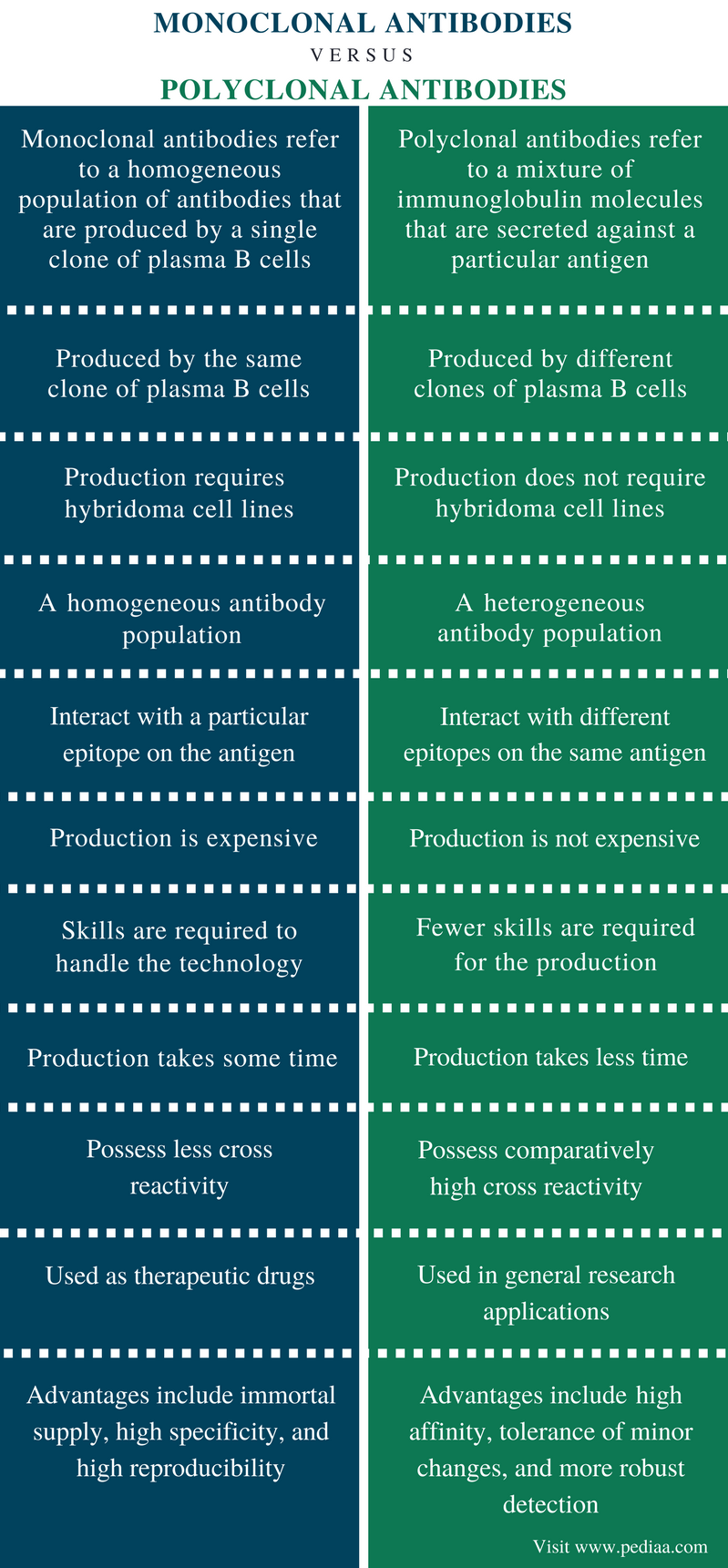
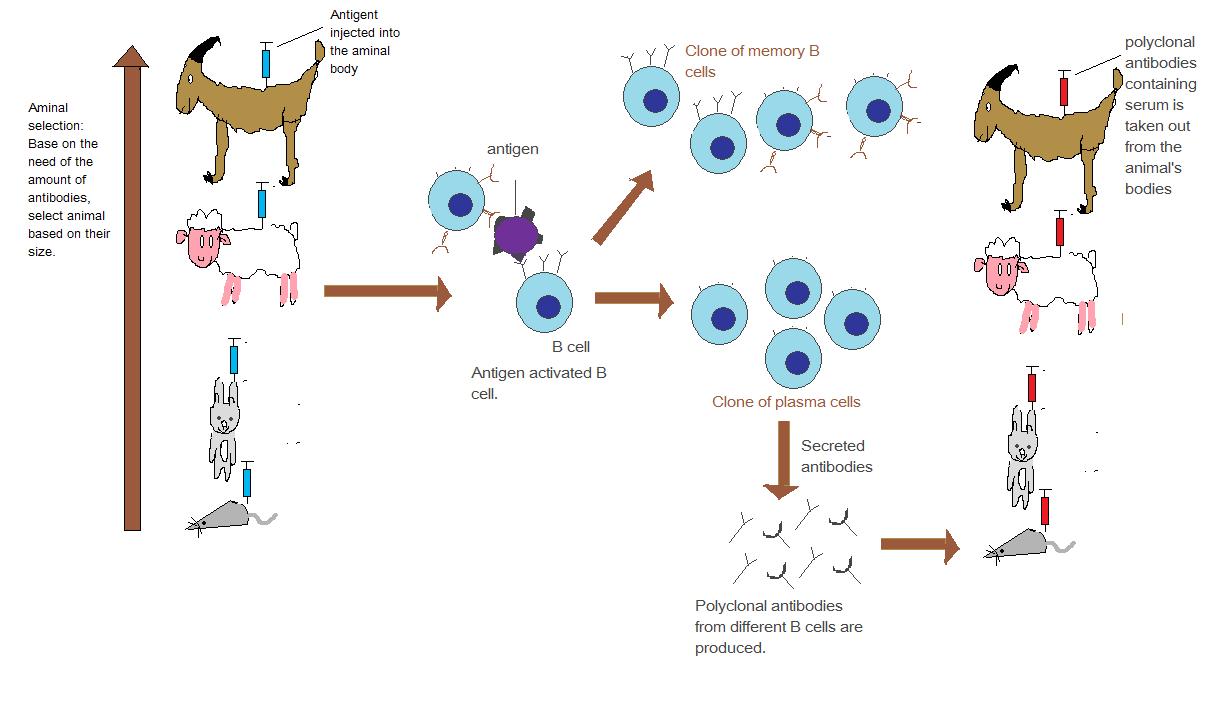
Monoclonal Antibodies In October 2008, the International Nonproprietary Name (INN) Working Group Meeting on Nomenclature for Monoclonal Antibodies (mAb) met to review and streamline the The present invention provides an improved method for the purification of monoclonal antibody from cell culture. Process of purification of the desired monoclonal antibody comprises affinity, hydrophobic interaction and optionally ion exchange column chromatography. It provides more than 99 purity of the desired monoclonal antibody. Due to their high specificity, monoclonal antibodies are excellent as the primary antibody in an assay and will often give significantly less background staining than polyclonal antibodies. Monoclonal Antibodies Michael Steinitz Editor Methods and Protocols Methods in this volume presents also a few review articles related to the topic of human monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies. Jerusalem, Israel Michael Steinitz Pref ace. Polyclonal Production For polyclonal antibodies to be produced, an antigen needs to be injected repeatedly over a long period, with several weeks intervening between successive doses. Polyclonal Antibodies Large quantities of polyclonal antibody are relatively quick and inexpensive to produce compared to monoclonal antibodies. They are non specific in that they are capable of recognising multiple epitopes on any one antigen. contrast, polyclonal antibodies bind to multiple epitopes and are usually made by several different plasma Wed, 26 Sep 2018 01: 12: 00 GMT Monoclonal antibody Download Books Monoclonal Antibodies 0 Pdf, Download Books Monoclonal Antibodies 0 For Free, Books Monoclonal Antibodies 0 To Read, Read Online Monoclonal Antibodies 0 Books. Monoclonal antibodies to treat cancer One way the immune system attacks foreign substances in the body is by making large numbers of antibodies. An antibody is a protein that sticks to a specific protein called an antigen. Production of monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies against a Nigerian isolate of banana streak virus Agindotan B. 3 1Biochemistry Department, University of Ibadan, Ibadan, Nigeria 2International Institute of Tropical Agriculture, Ibadan, Nigeria. page 211 emea 2009 guideline on development, production, characterisation and specifications for monoclonal antibodies and related products table of contents Polyclonal antibodies are synthesized from different immune cells and the antibodies produced bind to multiple antigens. List and types of monoclonal antibodies (FDA approved) Here is a list of examples some FDAapproved monoclonal antibody drugs. Monoclonal antibody (MAb) technology is well recognized as a significant development for producing specific serologic reagents to a wide variety of antigens in unlimited amounts. These reagents have provided the means for developing a number of highly specific and reproducible immunological assays. The monoclonal antibodies from ascitic fluids were purified and its reaction with rOMPw was assessed by ELISA. Polyclonal antibodies were also produced by immunization of rabbits PDF Monoclonal antibodies are essential tools for many molecular immunology investigations. In particular, when used in combination with techniques such as epitope mapping and molecular. Bagley 1 Monoclonal and Polyclonal Antibodies First studied as early as 1895, antibodies comprise an integral element of the human immune response to infection. The main difference between monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies is that monoclonal antibodies are produced by the same clone of plasma B cells, and they bind to a unique epitope whereas. Polyclonal antibodies (pAbs) are antibodies that are secreted by different B cell lineages within the body (whereas monoclonal antibodies come from a single cell lineage). They are a collection of immunoglobulin molecules that react against a specific antigen, each identifying a different epitope A Polyclonal Antibody represents a collection of antibodies from different B cells that recognize multiple epitopes on the same antigen. Each of these individual antibodies recognizes a unique epitope that is located on that antigen. Unlike polyclonal antibodies, which are produced in live animals, monoclonal antibodies are produced in vitro using tissueculture techniques. mAbs are produced by immunizing an animal, often a mouse, multiple times with a specific antigen. Monoclonal Antibodies: Methods and Protocols, Download book PDF. Protocols Table of contents (36 protocols) Epitope Mapping of Monoclonal and Polyclonal Antibodies Using Bacterial Cell Surface Display. AnnaLuisa Volk, Francis Jingxin Hu, Johan Rockberg. Antibodies are valuable tools in the laboratory and clinic. Antibodies include those secreted by a single clone of B lymphocytes, termed monoclonal antibodies, and those produced by a mixture of various B lymphocyte clones, termed polyclonal antibodies. Compared to polyclonal antibodies, homogeneity of monoclonal antibodies is very high. If experimental conditions are kept constant, results from monoclonal antibodies will. even if the original immunogen was impure affinity is defined and can be selected clean reagents giving low non specific binding and backgrounds indefinite supply of Ab with constant characteristics. The choice: monoclonal or polyclonal Advantages of monoclonal antibodies VITROS B12 monospecificity. Monoclonal antibodies (mAb or moAb) are antibodies that are made by identical immune cells that are all clones of a unique parent cell. Monoclonal antibodies can have monovalent affinity, in that they bind to the same epitope (the part of an antigen that is recognized by the antibody). In contrast, polyclonal antibodies bind to multiple epitopes and are usually made by several different plasma. Polyclonal and Monoclonal Antibodies 25 the antigen is a small chemical group, such as the hapten di or trinitrophenyl (DNP, TNP) that cannot be presented to T cells, the antigen will be unable to Antibodies, either monoclonal or polyclonal, raised against a purified tryptic fragment of uvomorulin recognize, in a detergent lysate of embryonal carcinoma cells metabolically labeled with 35S, three molecules (120, 100, and 88 kDa) that are not related, as judged by peptide mapping. Monoclonal antibodies (mAb) are used extensively in basic biomedical research, in diagnosis of disease, and in treatment of illnesses, such as infections and cancer. Antibodies are important tools used by Polyclonal antibodies may offer potential advantages in drug delivery. some antibody molecules may be degraded rapidly and excreted while others may have longer halflives. Bispecific antibodies immunoconjugate Polyclonal Antibodies After an antigen is injected into an animal by a regimen designed to induce an optimal immune response Serum can. Abcam's RabMAb technology combines the benefits of both monoclonal and polyclonal technology to create highly specific and sensitive rabbit monoclonal antibodies. Learn more about the advantages of RabMAb technology. Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) are complex proteins that specifically react with sites, or epitopes, on target molecules. They have become important research tools and are also a highly successful class of biological drugs. Production of Monoclonal Antibodies from Hybridomas in a Hollow Fiber Bioreactor contribute to the polyclonal response observed in antigen challenge. Prior thinking held that antibody production of monoclonal antibodies from hybridoma cell lines. monoclonal antibodies Hybridomas are hybrids between a nontransformed antibody producing B cell and a transformed cell (myeloma) that can grow continuously in culture. Differentiate among the categories: polyclonal, monoclonal, murine, chimeric, humanized and human antibodies. Discuss the advantages and disadvantages in human use of murine, chimeric, humanized and human antibodies. Discuss the unique physical characteristics of polyclonal and, monoclonal murine chimeric, POLYCLONAL AND MONOCLONAL. Monoclonal Versus Polyclonal Antibodies: Distinguishing Characteristics, Applications, and Information Resources Neil S. Trudel, and Frances WeisGarcia between polyclonal and monoclonal antibodies, with respect to their function and use, are also addressed briefly. Unlike polyclonal antibodies, which are produced in live animals, monoclonal antibodies are produced in vitro using tissueculture techniques. mAbs are produced by immunizing an animal, often a mouse, multiple times with a specific antigen. Polyclonal antibodies against PGCP have been prepared [8, 14, but antibodies are also commercially available. PGCP can be distinguished from glutamate carboxypeptidase II ( Chapter 367 ) using antibodies; however, glutamate carboxypeptidase II is a membrane protein. Monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies, known to inhibit elastase in vitro, were employed in an immunocompromised mouse model of invasive aspergillosis to determine if the antibodies could protect mice from fatal infection. Secondary Antibodies, Conjugates and Kits. Secondary antibodies are polyclonal or monoclonal antibodies that bind to primary antibodies or antibody fragments, such as the Fc or Fab regions. MONOCLONAL AND POLYCLONAL ANTIBODIES FOR IMMUNOASSAY INTRODUCTION J. Brown and Ian Weeks Department of Medical Biochemistry A selective list of applications in which polyclonal (PAbs), monoclonal antibodies (MAbs), their fragments and conjugates, which either play an essential role or have had a significant impact in basic research or the clinic. PRODUCTION AND QUALITY CONTROL OF MONOCLONAL ANTIBODIES 1. INTRODUCTION In this document the requirements for murine, human and engineered monoclonal antibodies for therapeutic (including ex vivo application) and in vivo diagnostic use in humans are outlined. Monoclonal antibodies intended for use in the purification of other monoclonal or polyclonal antibodies are commercially available. Therefore, the objective of this study was to produce and characterize new polyclonal and monoclonal antibodies against L. intracellularis that are suitable for diagnostic use. Monoclonal antibodies are antibodies that are made by identical immune cells that are all clones of a unique parent cell and bind to the same epitope. Given almost any substance, it is possible to produce monoclonal antibodies that specifically bind to that substance; they can then serve to detect or purify that substance. This has become an important tool in biochemistry, molecular biology and. Polyclonal and monoclonal antibodies are used in a wide range of in vitro assays in many different formats. The formats of the technology range from sophisticated flow cytometry (FCM) to simple enzymelinked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Pohanka: Monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies production 116 Crossreactivity is the interaction between the paratope of an antibody and a similar epitope or or monoclonal, antibodies with a defined specificity was a longstanding goal of immunochemical research. This goal was achieved with the development of the technology for hybridoma production. Monoclonal Versus Polyclonal Antibodies SEPTEMBER 29, 2015 BY NICK FEO (EDIT) Introduction Antibodies are protein molecules used to by the immune system to combat pathogens. Genetically Engineered Antibodies In addition to traditional monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies targeted against specific proteins, there are other means of antibody generation and protein detection available as the result of numerous advances in genetic engineering technology..