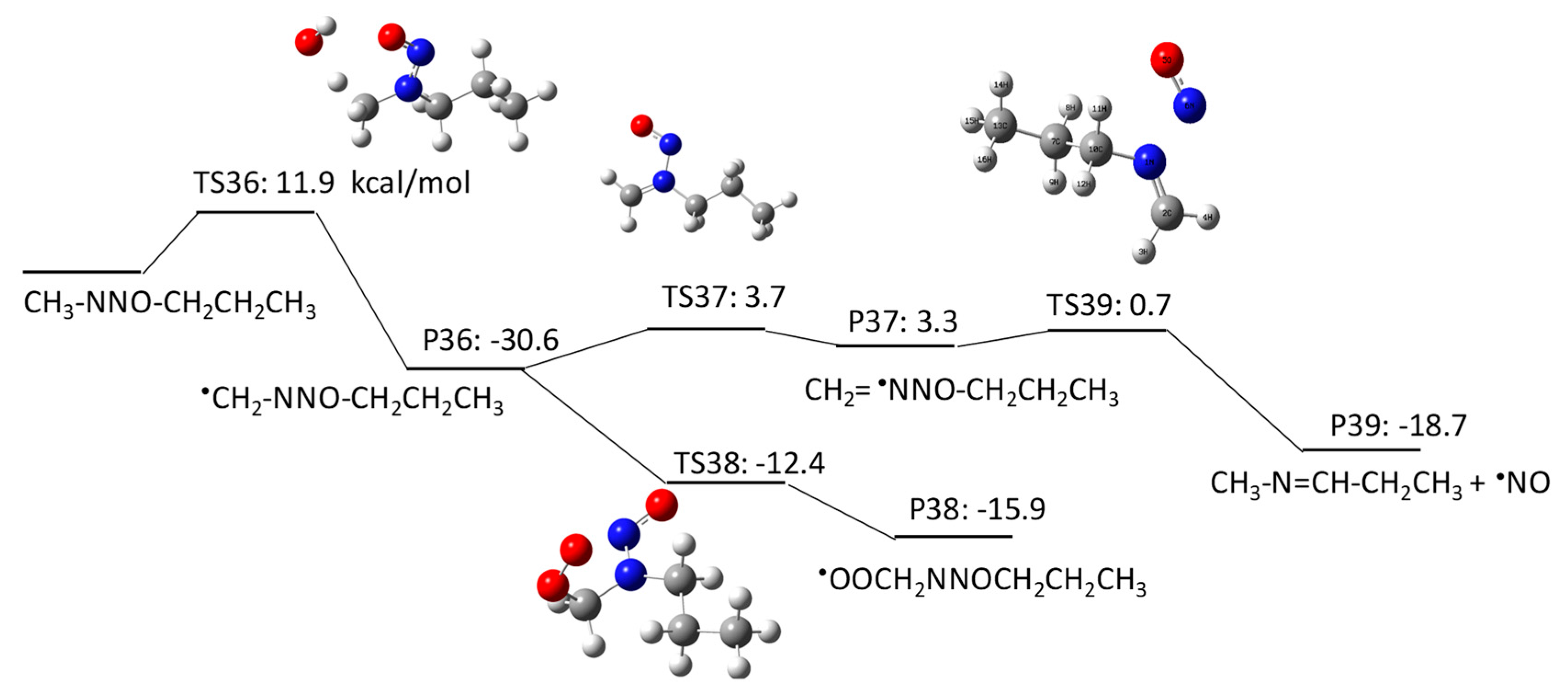
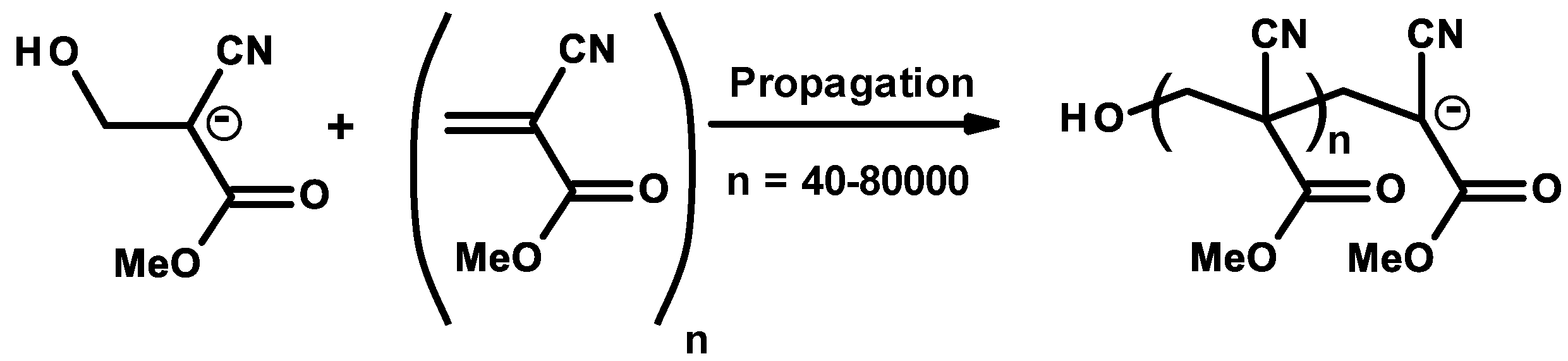
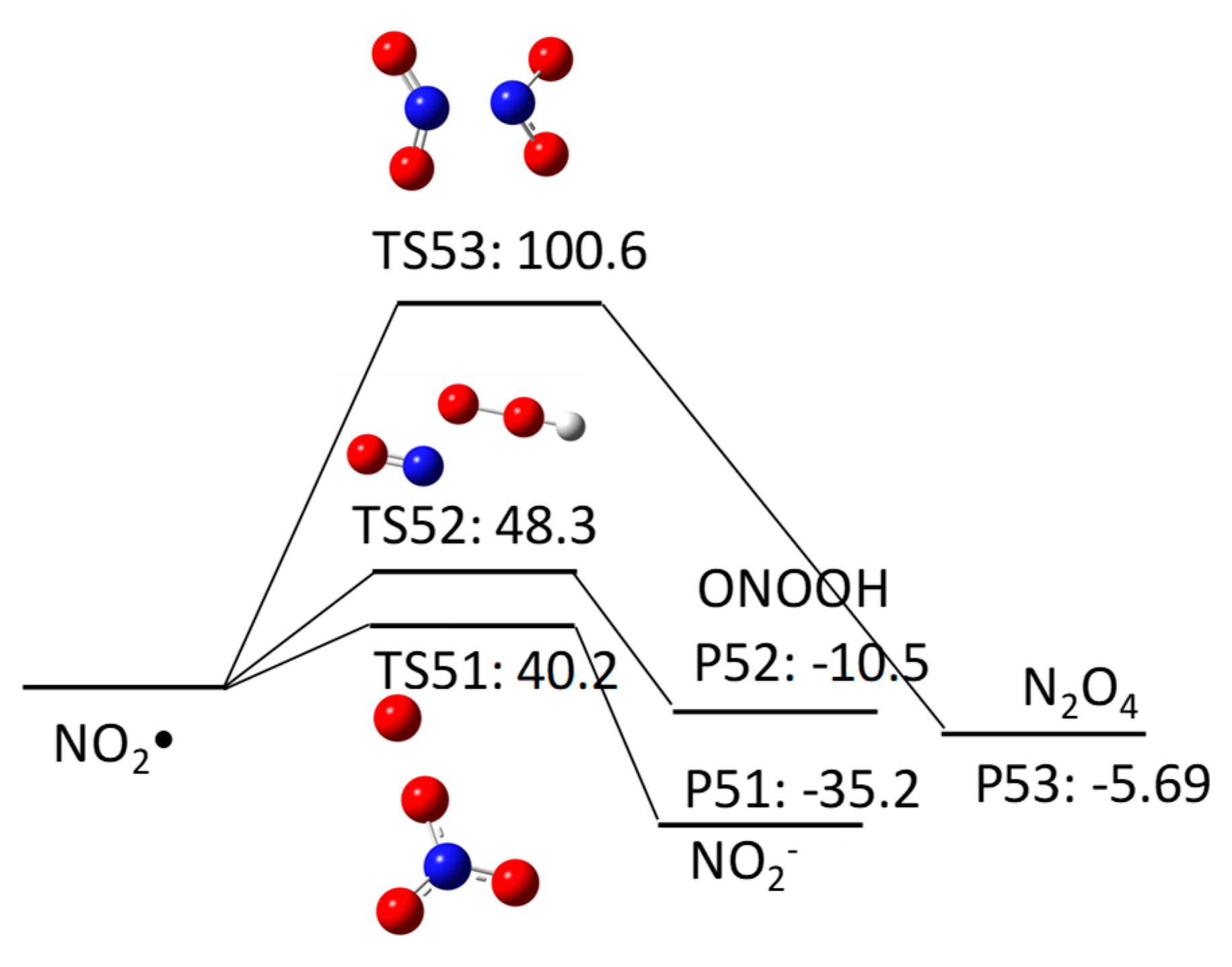
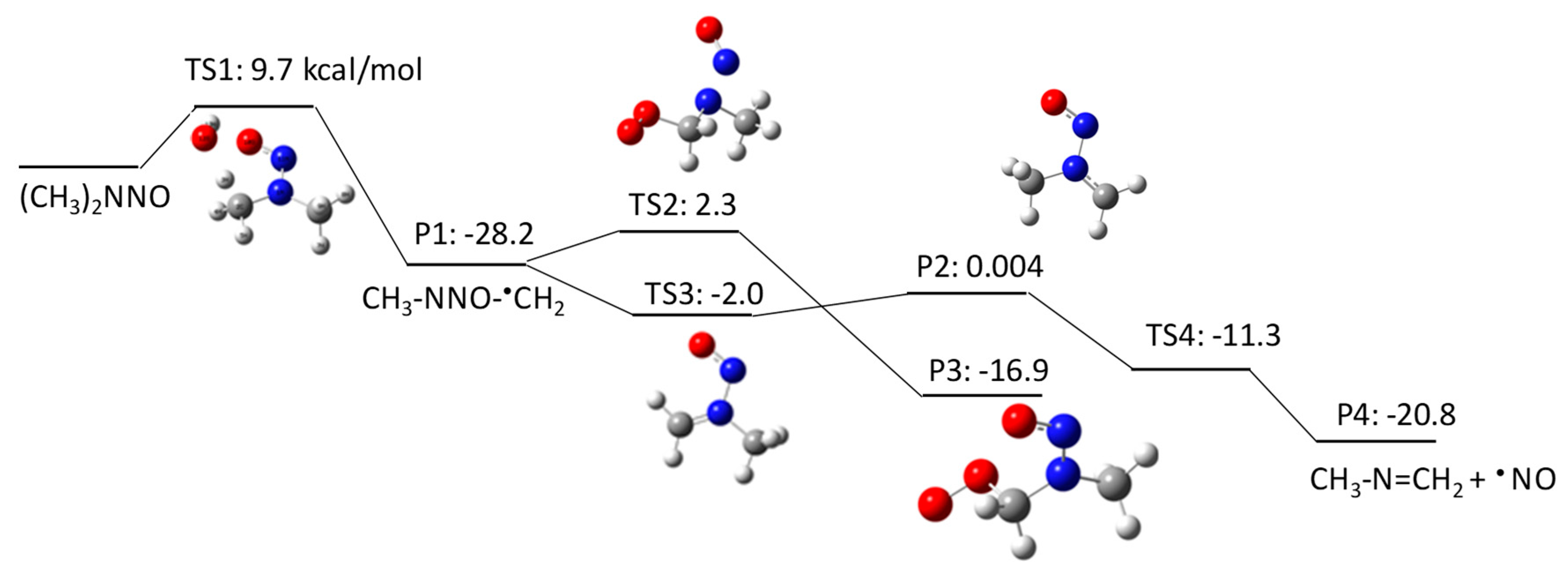
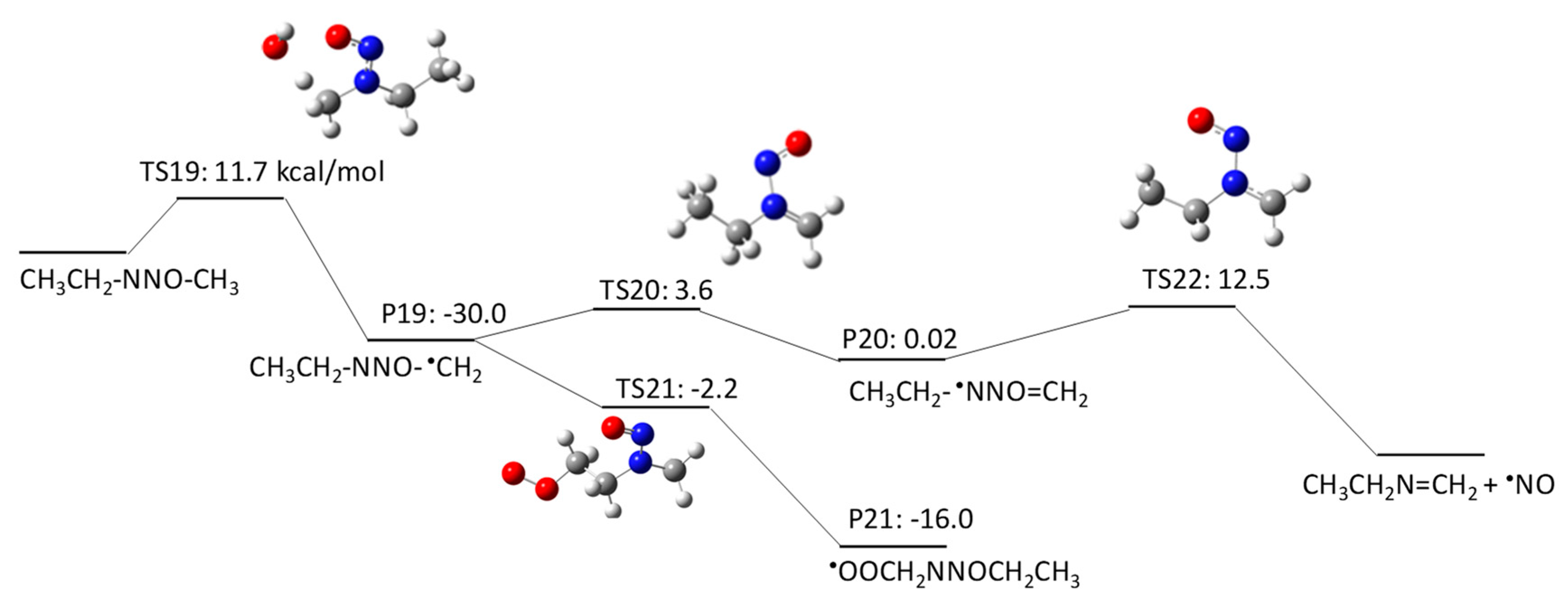
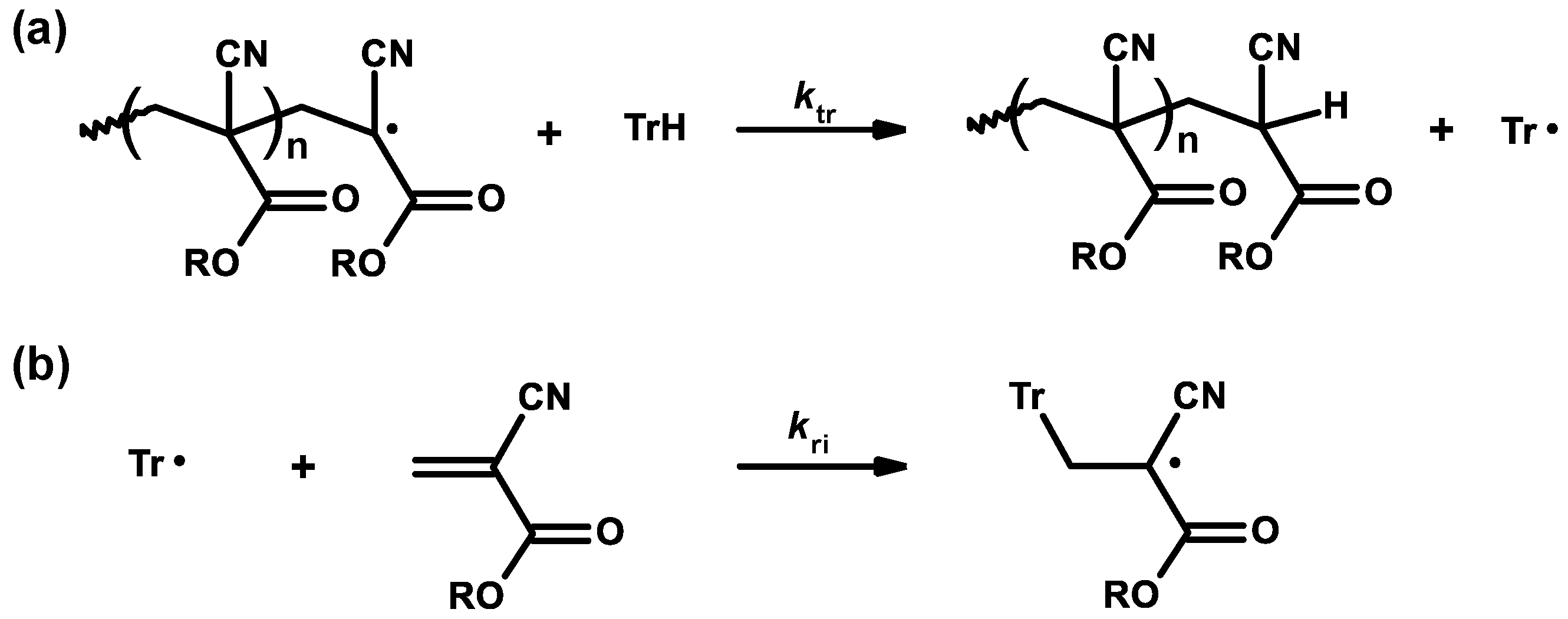
The aim of this Encyclopedia is to offer for the first time a description of free radicals within an interdisciplinary and multidisciplinary context, connecting structural characteristics and chemical properties to their applications in different areas of chemistry and related disciplines. Three of the new species created are radicals: HO, H, Radiation Chemistry Page 14 of 19. 55 Principles of Radiation Interactions Direct Action, Indirect Action and the Oxygen Effect So far, the radiation chemistry of water has been considered. : Chemistry of hydrogen oxide radicals (HOx) in the Arctic spring 1 Introduction Radiative forcing by aerosol and tropospheric ozone pollution transported from. radicals, such as hydrated electrons, hydrogen atoms, and hydroxyl radicals. Because of the high time resolution of these techniques, absorption spectra and redox properties of these inorganic radicals could Small video on free radicals explaining what are free radicals, its properties and the factors it depends on. Also the STABILITY OF FREE RADICALS is explained. Radicals chemistry pdf Moses Gomberg, the founder of radical chemistry. Progress in Inorganic Chemistry PDF. Propose mechanisms for free radical reactions, and predict and explain experimental results Which of the following free radicals is the most stable? (CH 3 CH 2)3 C B Organic Chemistry 2210 Answer All Questions 1. Which of the following compounds is a product of the reaction shown? F H knowledge, organic chemistry of ion radicals is now entering the third stage of develop ment, namely, putting the ideas elaborated into general operation, including them in. highly useful and selective reactions, and their chemistry offers a viable alternative to traditional, ionic methods. Advantages of radicals (i) Radicals are neutral and so. Elements [or radicals with valency one are monovalent, those with valency two are divalent, and those with valency three are trivalent. All nonmetals and nonmetallic radicals have negative valencies as shown in the table below. FreeRadical Chemistry 1 THE CHEMISTRY OF FREE RADICALS Barry Halliwell Division of Pulmonary Critical Care Medicine, V. Davis Medical Center, Sacramento, California. Special Issue Radical Chemistry PDF Fulltext (4206 KB) HTML Fulltext XML Full (shorter than 1 ps) is the precursor of these radicals in aqueous solutions, its chemistry is usually known to be limited to the reaction of proton transfer by forming OH. Free radicals in chemistry, biology and medicine: contribution of radiation chemistry S69 to bond to electron rich centers (S, O, N, Cl, Br, I, P) to form 2c3e bonds [4, 5. Radical theory is an obsolete scientific theory in chemistry describing the structure of organic compounds. The theory was pioneered by Justus von Liebig, Friedrich Whler and Auguste Laurent around 1830 and is not related to the modern understanding of free radicals. Freeradical chemistry of sulfite. as are the kinetics of the reactions of the sulfitederived radicals SO3 and the peroxy derivative SO5 with organic compounds. Full text Full text is available as a scanned copy of the original print version. Get a printable copy (PDF file) of the complete article. PDF This article reviews the progress in the area of radicals in carbohydrate chemistry with special attention to new developments published during the past decade. 2 Three Fates of Radicals: a) Addition to pi bond Br C Br H The bromine radical and one electron from a pi bond form a new bond on the least substituted end of the alkene. The other electron in the pi bond is transferred to the more stable carbon atom (making a Radical: Radical, , in chemistry, molecule that contains at least one unpaired electron. Most molecules contain even numbers of electrons, and the covalent chemical bonds holding the atoms together within a molecule normally consist of pairs of electrons jointly shared by the atoms linked by the bond. Most 2nd PUC Chemistry Jan 2016. Free Radicals A free radical is a species containing one or more unpaired electrons. Free radicals are electron Documents Similar To Chemistry Notes Class 11 Chapter 13 Hydrocarbons. NOxy Radical Chemistry Toward Application for Efficient Catalysis Today [s Contents 2 1. Fundamentals of NOxy Radical Species 4. Iminoxyl RadicalMediated Reactions 5. Perspectives But, some radicals are stable to isolate or generatable although transient. NPTEL Chemistry Principles of Organic Synthesis Lecture 21 FreeRadical Reactions I 9. 1 Principles Free radicals may be defined as the species that contain one or more unpaired electrons. They are generally less stable and react in fraction of seconds with another species. In chemistry, a radical (mair precisely, a free radical) is an atom, molecule, or ion that haes unpaired valence electrons. Wi some exceptions, thir unpaired electrons mak free radicals heichly chemically reactive taewart ither substances, or even taewart themsels: thair molecules will eften spontaneously dimerise or polymerise if thay come in contact wi each ither. PDF ABSTRACT In recent years, there has been a large quantity of attention toward the field of free radical chemistry. Free radicals react (ROS) and reactive nitrogen species(RNS) are generated. The last 1015 years have seen the development of free radical chemistry in organic synthesis Major obstacle is the ability of radicals to react with themselves Overcome by only having a very low concentration of radicals present in a reaction Free radicals play an important role in combustion, atmospheric chemistry, polymerization, plasma chemistry, biochemistry, and many other chemical processes. In living organisms, the free radicals superoxide and nitric oxide and their reaction products regulate many processes, such as control of vascular tone and thus blood pressure. 1, 4Hydrogen transfer from the 1hydroxyallyl radical to give the enoxyl (keto) radical is an exothermic process with a high activation energy based on DFT calculations. Thiyl Radicals in Organic Synthesis When burned, sulfur melts to a bloodred liquid and emits a blue ame that is best observed in the dark. Jian Jin FREE online interactive quizzes on Chemical Symbols of Radicals Quiz Activities, Worksheets, Exercises Problems in Chemistry for School and College students with theory Radical (chemistry) In chemistry, radicals (often referred to as free radicals) are atomic or molecular species with unpaired electrons on an otherwise open shell configuration. The aim of this Encyclopedia is to offer for the first time a description of free radicals within an interdisciplinary and multidisciplinary context, connecting structural characteristics and chemical properties to their applications in different areas of chemistry and related disciplines. Wiley Online Library will be unavailable on Saturday 01st July from EDT and on Sunday 2nd July EDT for essential maintenance. Free Radical Reactions A free radical is a species containing one or more unpaired electrons. Free radicals are electrondeficient species, but they are usually uncharged, so their chemistry is very different from the chemistry of evenelectron electrondeficient species such as carbocations and Some Basic Concepts in Radical Chemistry Radicals are species (atoms, molecules, ions) which contain an unpaired electron, R. 2 Elementary Radical Reactions The chemistry of the resultant radical cation is determined from the functionality around its periphery. Deprotonation of the radical cation is a major pathway, resulting in a radical which adheres to typical radical reactivity patterns. txt) or view presentation slides online. Scribd is the world's largest social reading and publishing site. pdf from CHEMISTRY 20 at Ho Chi Minh City University of Natural Sciences. 2nd YEAR ORGANIC CHEMISTRY TUTORIAL SHEET Radicals Reading: Lecture. The chlorine molecule Cl 2 undergoes homolysis in ultraviolet light to form two Cl. These are electrically neutral and highly reactive. We carried out a survey of the relative reactivity of a collection of 91 neutral boryl radicals using density functional calculations. Their reactivities were characterized by four indices, i. , the global electrophilicity, global nucleophilicity, local electrophilicity, and local nucleophilicity. Unit 5: Radicals and Radical Reactions. Introduction Free radicals can be defined as chemical species which have a single unpaired electron. In the important case (for organic chemistry) of the methyl radical, the radical center is trivalent and trigonally hybridized (Scheme 1). More commonly, in the laboratory, radical chemistry is. Group I Radicals which are detected by dilute H2SO4 or dilute HCl, by liberating a gas (i) Carbonate (ii) Sulphite (iii) Sulphide (iv) Nitrite (v) Acetate Group II Radicals Review A study of free radical chemistry: their role and pathophysiological significance Mariusz Gutowski1 and Sawomir Kowalczyk2 1Neurovascular Research Laboratory, Faculty of Health, Science and Sport, University of Glamorgan, UK; 2Department of Microbiology, Faculty of Pharmacy, Poznan University of Medical Sciences, Pozna, Poland from Organic Chemistry by Robert C. Professor of Chemistry, emeritus University of California, Riverside Important free radicals that we see in this chapter include halogen atoms (X. ), and carbon free radicals (R3C. GRE Chemistry Test Practice Book This practice book contains n. Become familiar with Radical Fates Radicals desire to become more stable. Radical Fate# 1: Add to a pi bond Trade pi bond (weaker) for sigma bond (stronger) Radical desires one electron to fill octet. THE CHEMISTRY OFACYL RADICALS TULLIO CARONNA AND FRANCESCO MINISCI Istituto di Chimica del Politecnico di Milano Milano Piazza Leonardo da Vinci Italy 263. INTRODUCTION Acyl radicals, RCO, are one of the basic classes of carbon free radicals. in biomedical sciences and is a science writer, educator, and consultant. She has taught science courses at the high school, college, and graduate levels. LANGE'S HANDBOOK OF CHEMISTRY John A. Dean Professor Emeritus of Chemistry University of Tennessee, Knoxville Fifteenth Edition Properties of Atoms, Radicals, and Bonds, have been signicantly enlarged. For example, the entries under Ionization Energy of Molecular Oxygen Radicals and Related Species 5 protectors against irradiation, such as glutathione and ethanol, protected against oxygen toxicity, or as currently defined, they acted as antioxidants. Another pioneer was Denham Harman, who proposed in 1954 that aging was a consequence of free radical attack on Over the past few years, radical chemistry has witnessed a rapid development, with the result, for example, that new methods for producing radicals now allow the targeted use of these reactive intermediate stages in organic synthesis..