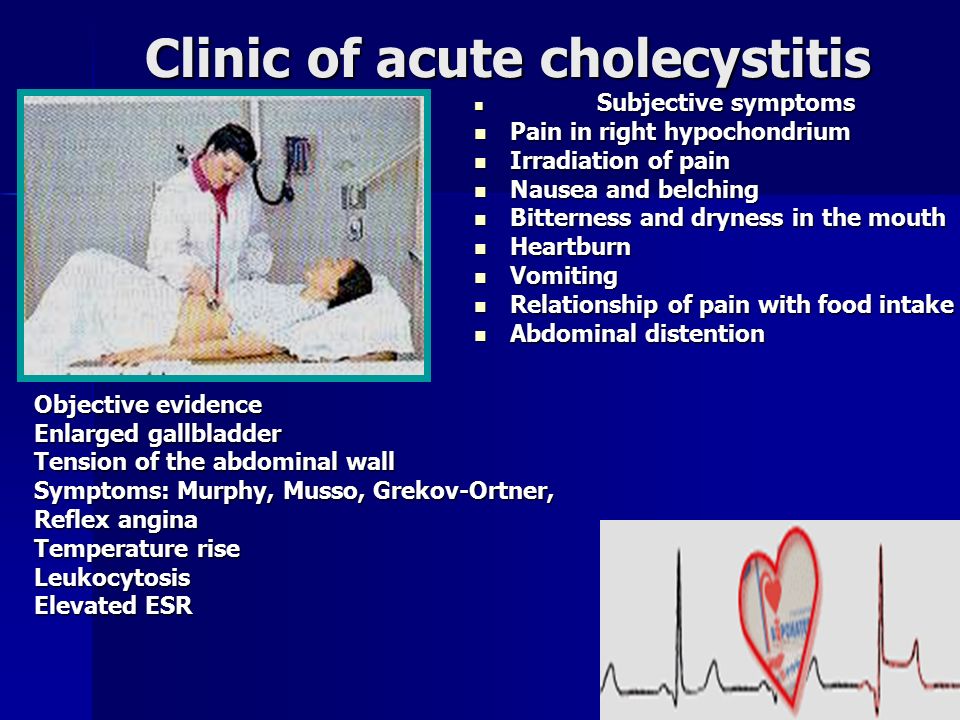
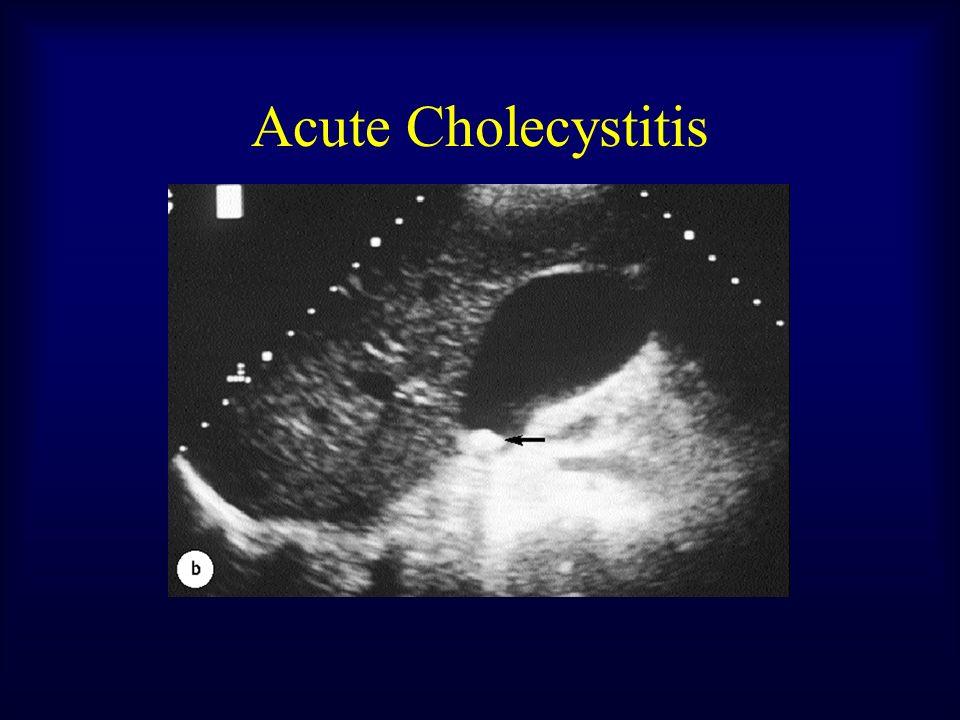
Acute acalculous cholecystitis due to Vibrio cholerae. Previous Article Normothermic versus hypothermic coronary bypass surgery. PPT; Hide Caption Download See figure in Article. Download Hires image; Download. Acalculous cholecystitis is a severe illness that is a complication of various other medical or surgical conditions. Duncan first recognized it in 1844 when a fatal case of acalculous cholecystitis complicating an incarcerated hernia was reported. Acute acalculous cholecystitis is a lifethreatening condition with a mortality of up to 50. Acute cholecystitis should be suspected when someone presents with: A history of suddenonset, constant, severe pain in the upper right quadrant, lasting several hours. Acute acalculous cholecystitis is an acute inflammation of the gallbladder in the absence of gallstones and accounts for 5 to 10 of all cases of acute cholecystitis. Acalculous cholecystitis is a less common, but usually more serious, type of acute cholecystitis. It usually develops as a complication of a serious illness, infection or injury that damages the gallbladder. Acute acalculous cholecystitis associated with gallbladder perforation is often seen with severe infections like pneumonia, viral infections, and with enteric fever where the causative organism Salmonella typhii was identified in bile and are further concentrated in gallbladder (7). Acute Acalculous Cholecystitis Download as Powerpoint Presentation (. txt) or view presentation slides online. Scribd is the world's largest social reading and publishing site. INTRODUCTION Acute cholecystitis is a syndrome of right upper quadrant pain, fever, and leukocytosis associated with gallbladder inflammation. It typically occurs in patients with gallstones (ie, acute calculous cholecystitis), while acalculous cholecystitis accounts for a. Cholecystitis: Cholecystitis, acute or chronic inflammation of the gallbladder, in most instances associated with the presence of gallstones. Diseasecausing bacteria such as Salmonella, Staphylococcus, Streptococcus, and Leptospira are usually found in cases of acute inflammation, and they are also found in Acalculous cholecystitis may cause hemorrhage through mucosal necrosis and ulceration with erosion into one or more vessels. Our patients did not present with GI bleeding as a primary symptom. The first patient had symptoms, signs, and laboratory studies that suggested choledocholithiasis. Acute cholecystitis is an inflammation of the gallbladder. The gallbladder is an organ that sits below your liver and helps your body digest fat. On the other hand, there is another type of acute cholecystitis, acute acalculous cholecystitis, in which stones are not involved as causative factors. Risk factors for acute acalculous cholecystitis include surgery, trauma, burn, and parenteral nutrition. ACUTE CHOLECYSTITIS Pableo, Rachel M. Female Married Roman Catholic August 4, 1966 Solana, Cagayan July 29, 2010 Chief complaint Right upper quadrant Introduction. Acute cholecystitis is a very common complication of cholelithiasis, and as such is frequently encountered in surgical practice [14. There were no diagnostic criteria or severity assessment criteria for this common disease until 2007. ACUTE CHOLECYSTITIS Assistant professor: pechyonkin Student: raza sarif Group: 414 A Slideshare uses cookies to improve functionality and performance, and to provide you with relevant advertising. If you continue browsing the site, you agree to the use of cookies on this website. This feature is not available right now. acalculous cholecystitis is still \1irvis ef. (15) showed that sonography and CT are t 0 specific and sensitive for diagnosing acute Acute Acalculous Cholecystitis Download as Powerpoint Presentation (. txt) or view presentation slides online. Dengue Fever (DF) with acute acalculous cholecystitis is a rare and atypical presentation. We report a case of dengue fever presenting as acute acalculous cholecystitis. Acute cholecystitis refers to the acute inflammation of the gallbladder. It is the primary complication of cholelithiasis and the most common cause of acute pain in the right upper quadrant (RUQ). Herein, we describe a rare case of acute acalculous cholecystitis (AAC) that developed in a 36yearold man after an Indian cobra (Naja naja) bite in the absence of any other predisposing factors for AAC. The probable mechanisms for the occurrence of AAC have been highlighted. Chronic (a) Secondary chronic cholecystitis (b) Primary chronic cholecystitis ACUTE CHOLECYSTITIS: 90 associated calculi PATHOLOGY. Acute cholecystitis is sudden swelling and irritation of the gallbladder. The gallbladder is an organ that sits below the liver. It stores bile, which your body uses to digest fats in the small intestine. 510 acute cholecystitisChronic form: biliary symptoms without gallstones Often called biliary dyskinesiaUp to 1015 laparoscopic cholecystectomies. Acalculous cholecystitis is a severe illness that is a complication of various other medical or surgical conditions. Duncan first recognized it in 1844 when a fatal case of acalculous cholecystitis complicating an incarcerated hernia was reported. Some form of gallbladder involvement is present in 50 to 98 of all cases with viral hepatitis [3, but the pathophysiology behind it is still unclear. Acute calculus cholecystitis is a very common disease with several area of uncertainty. The World Society of Emergency Surgery developed extensive guidelines in order to cover grey areas. acute cholecystitis and multisystem organ failure, significant cardiovascular disease, or between acalculous and calculous cholecystitis. The latter is a result of biliary stasis from critical illness, whereas calculous cholecystitis is a result of true luminal obstruction. The pathogenesis of acute cholecystitis is primarily due to obstruction of biliary outflow by a stone. Other rare causes may be stricture, kinking of the cystic duct, intussusception of a polyp, torsion of the gallbladder, pressure of an overlying lymph node on the cystic. Acute cholecystitis is inflammation of gallbladder. After frequency this disease takes second place after appendicitis and makes about 10 in relation to all acute surgical diseases of organs of abdominal cavity. Anatomy, and is known as acute acalculous cholecystitis. Acalculous cholecystitis is an acute necroinflammatory disease of the gallbladder with a multifactorial pathogenesis. It accounts for approximately 10 percent of all cases of acute cholecystitis and is associated with high morbidity and mortality rates. Prognosis good with treatment Classification of Acute Cholecystitis Two categories: 1. acute calculous cholecystitis 2. acute acalculous cholecystitis Causes In 95 of cases, acute cholecystitis is caused by gallstones in the gallbladder. Other causes include severe illness and (rarely) tumors of the gallbladder. Harvest Time Acute and Chronic Cholecystitis and Cholelithiasis CLINICAL MANIFESTATION KOLESISTITIS AKUT Adalah reaksi inflamasi akut dinding kandung empedu dgn ditandai Cholecystitis powerpoint presentation Healthy young person with fever, malaise, myalgias viral hepatitis (try to locate source). However, decreased inf with hepatitis viruses A, B, C in last. Although recognized for more than 150 years, acute acalculous cholecystitis (AAC) remains an elusive diagnosis. This is likely because of the complex clinical setting in which this entity develops, the lack of large prospective controlled trials that evaluate various diagnostic modalities, and thus dependence on a small data base for clinical decision making. Clinical Guideline for Management of Acute Cholecystitis in Adults Page 1 of 9 Clinical Guideline for Management of Acute Cholecystitis in Adults 3. Acalculous cholecystitis o This can account for around 10 of cases of acute cholecystitis. Initial management Acute acalculous cholecystitis is a life threatening condition that occurs in critically ill patients; it accounts for 514 of all cases of cholecystitis. The diagnosis is often elusive and is associated with considerable mortality (up to 50). Additional educational resources. In Laproscopic surgery, Fellow in Robotic Lap. Acute acalculous cholecystitis In 510 of cases of acute cholecystitis Seen in critically ill pts or prolonged TPN More likely to progress to gangrene, empyema, perforation due to ischemia Caused by gallbladder stasis from lack. Gallbladder wall inflammation usually follows obstruction of the cystic duct by a stone. Inflammatory response can be evoked by three factors. Slideshow by dillian Rarely, acute cholecystitis occurs in a person without gallstones (acalculous cholecystitis). Acalculous cholecystitis is a serious disease. It tends to occur after major injuries, operations, burns, bodywide infections (sepsis), and critical in people receiving prolonged intravenous feedings. and acute acalculous cholecystitis), chronic cholecystitis, emphysematous cholecystitis and xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis. Ultrasound is the primary imaging tool because it has high sensitivity in the detection Acute Cholecystitis: Acute Cholecystitis Acute calculous cholecystitis 90 Acute acalculous cholecystitis No gallstone Gall bladder coated by fibrinous exudate. Mucosa congested, lumen filled with pus and green bile. An acute acalculous cholecystitis is a potential manifestation of leptospirosis. Rafting is a wellknown risk factor for leptospirosis. Acute acalculous cholecystitis secondary to dengue fever Farah HISAMONIE KOH 1, Hartini MISLI 2, Vui Heng CHONG 2 1 Medical School, Queensland University, Australia, 2 Department of Medicine. Cholecystitis is inflammation of the gallbladder. Symptoms include right upper abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and occasionally fever. Often gallbladder attacks (biliary colic) precede acute cholecystitis. The pain lasts longer in cholecystitis than in a typical gallbladder attack. Without appropriate treatment, recurrent episodes of cholecystitis are common. Acute cholecystitis can develop without gallstones in critically ill or injured patients. However, the development of acute acalculous cholecystitis is not limited to surgical or injured patients, or even to the intensive care unit. Diabetes, malignant disease, abdominal vasculitis, congestive heart. Cholecystitis is an inflammation of the gallbladder that usually occurs due to a gallstone getting stuck in the opening. It can be acute or chronic and may lead to abdominal bloating, nausea and.