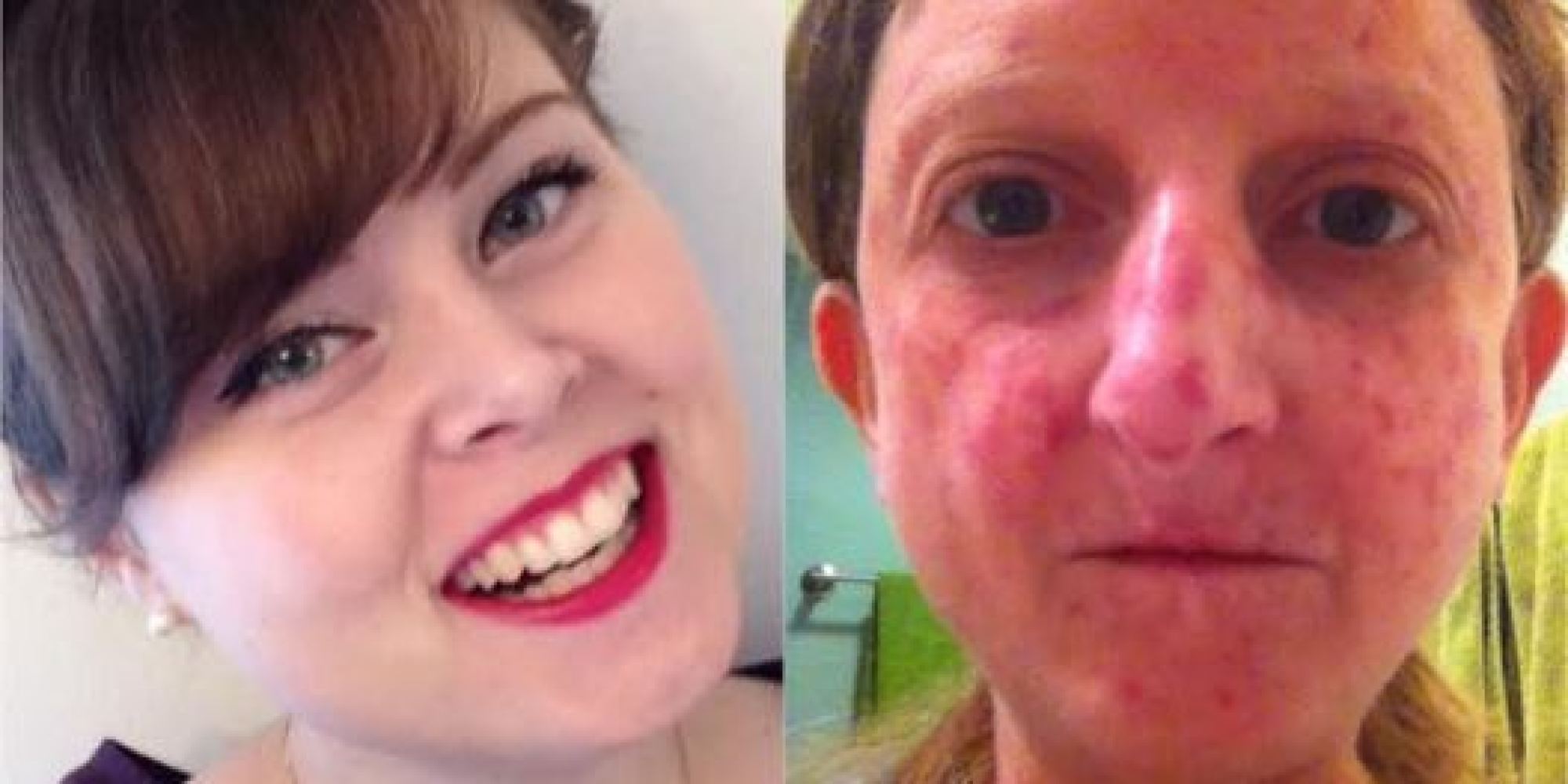
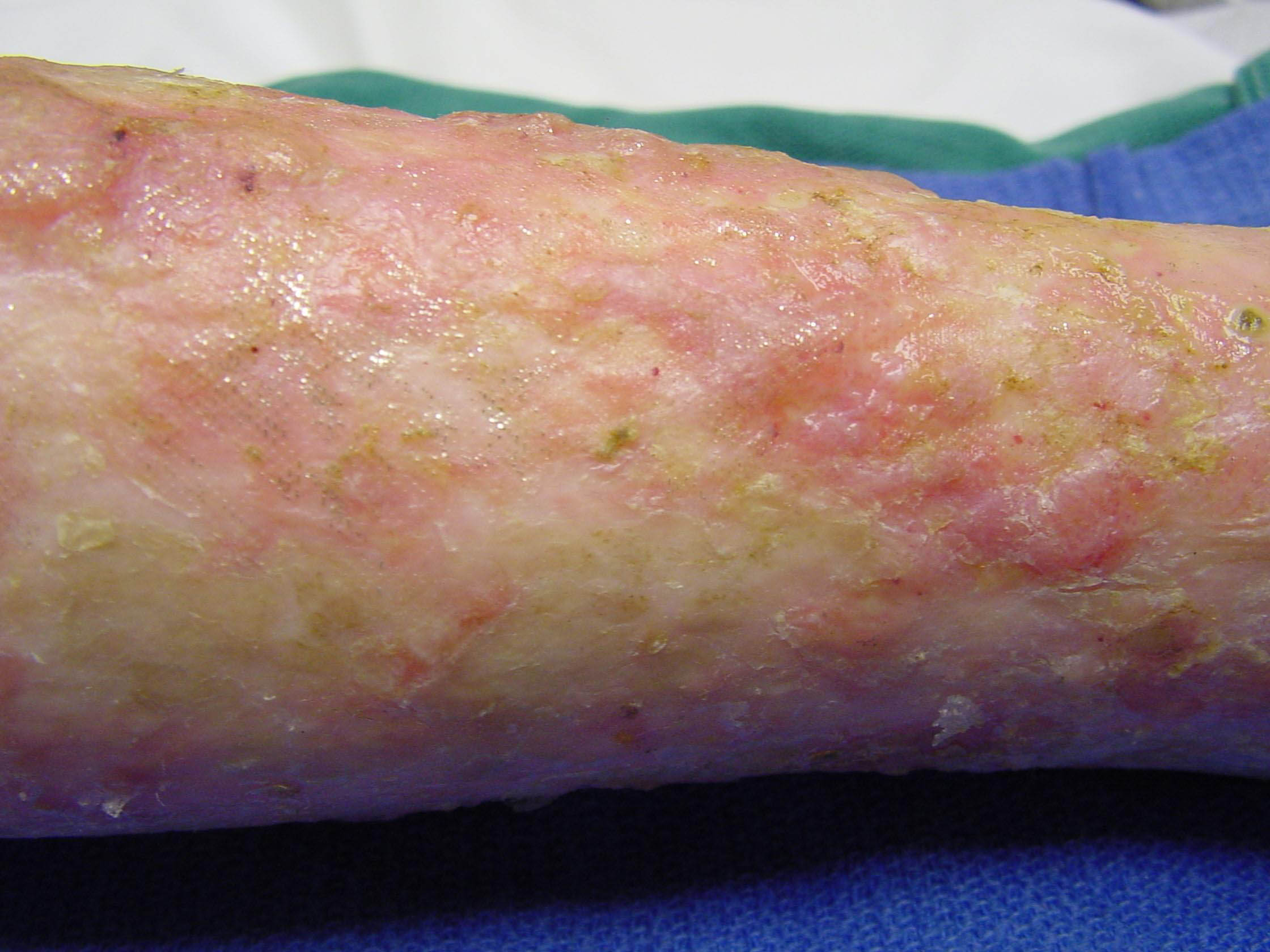
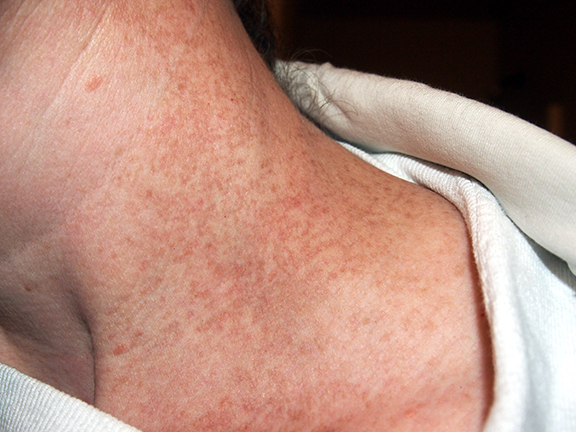
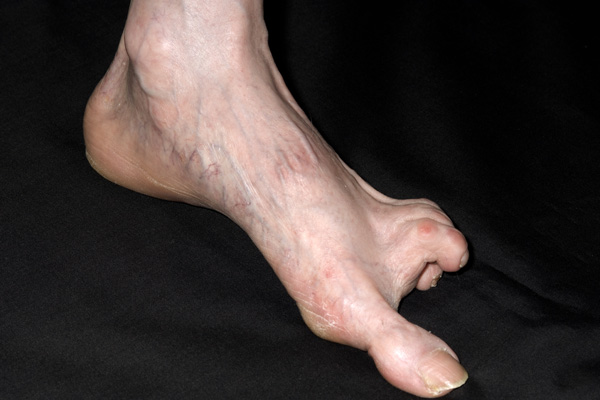
Diagnosis. Because scleroderma can take so many forms and affect so many different areas of the body, it can be difficult to diagnose. After a thorough physical exam, your doctor may suggest blood tests to check for elevated blood levels of certain antibodies produced by the immune system. It is a group of diseases that cause abnormal growth of connective tissue. Connective tissue is the material inside your body that gives your tissues their shape and helps keep them strong. Scleroderma is a disease of the immune system that scars and thickens the skin. Sometimes it damages the area around internal organs and blood vessels. It varies in severity from a mild form that most people can handle to lifethreatening. Evidence reviews Prazosin for Raynaud's phenomenon in progressive systemic sclerosis. Scleroderma is a connective tissue disease causing fibrosis and commonly affects the skin and internal organs such as the GI tract, lungs, kidney and heart. Scleroderma is a poorly understood illness that causes widespread hardening of the skin, especially on the hands and face. It also can damage the lungs, heart, kidneys, digestive tract, muscles and. Scleroderma is an autoimmune condition of the connective tissue characterized by skin thickening, spontaneous scarring, blood vessel disease, and varying degrees of inflammation, associated with an overactive immune system. Symptoms of scleroderma include hardening of the skin and Raynaud's disease, a response in the fingers or toes to cold temperatures, states Mayo Clinic. The symptoms of scleroderma depend on what part of the body is affected, but can also include lifethreatening changes in the kidneys and the heart. Limited Scleroderma CREST Syndrome Limited scleroderma means only limited areas of skin are thick; usually just the fingers andor face. Limited scleroderma is the milder form of scleroderma. It is more common among Caucasians than other populations. Every person with scleroderma is different and has a different pattern of symptoms. We are SRUK, the UKs only charity dedicated to improving the lives of people with scleroderma and Raynauds phenomenon. Scleroderma is a complex, multisystem disease that often progressively affects the skin, blood vessels, lungs, gastrointestinal tract, kidneys, heart, and musculoskeletal tissues. Systemic sclerosis (SS) is an autoimmune disorder. This means its a condition in which the immune system attacks the body. Healthy tissue is destroyed because the immune system mistakenly. Scleroderma definition, a disease in which connective tissue anywhere in the body becomes hardened and rigid. Scleroderma is a disease in which the skin becomes progressively hard and thickened. This occurs when immune cells activate, producing scar tissue in the skin, internal organs, and small blood vessels. The word scleroderma means hard skin and is believed to be caused by an overproduction of collagen. Like most forms of Myositis, it is considered a chronic, autoimmune disease primarily affecting the connective tissue, which is tissue that supports organs and other parts of the body. Systemic scleroderma, also called systemic sclerosis (SSc), is a multisystem autoimmune disease characterized by the accumulation of scar tissue in the skin and several internal organs such as the heart, kidney, lungs, and gastrointestinal tract. Risk factors for systemic scleroderma. Most patients develop systemic scleroderma in their 30s or 40s. The exact cause of the disease is unknown. No capable doctor will ever recommend the same treatment regimen to every patient suffering from the same ailment. Thats because every case of a single type of disease can be wildly different and people tend to respond in different ways to each treatment type. Systemic sclerosis (SSc) is a multisystem autoimmune disease in which there is increased fibroblast activity resulting in abnormal growth of connective tissue. This causes vascular damage and fibrosis. Fibrosis occurs in skin, the gastrointestinal (GI) tract, heart, lungs and other internal organs. A discussion of the different kinds of scleroderma (localized versus diffuse systemic versus limited systemic forms); the epidemiology of scleroderma in terms of prevalence and incidence; plus. Scleroderma is a rare form of arthritis. There are many types, with a wide range of causes, symptoms, severity, and treatments. To begin, watch our Video Series for clearcut examples and symptoms. Then explore diagnosis, symptoms, treatments and clinical trials in our Medical Directory. We also offer very broad coverage for many related or overlapping illnesses, such as Autoimmune Diseases. Scleroderma is an uncommon condition that results in hard, thickened areas of skin and sometimes problems with internal organs and blood vessels. The Scleroderma Foundation's 2018 Outstanding National Advocate Award recognized Dee Burlile and Shelley Van Pelt, whose passion and commitment have had a significant impact. Early symptoms of scleroderma can vary for each person, and often depend on the type and subtype involved. Common symptoms include patches of thickened and abnormally colored skin and Raynaud's phenomenon (a disorder that affects the blood vessels in the fingers, toes, ears, and nose). The term scleroderma is derived from the Greek words skleros (hard or indurated) and derma (skin) and it is used to describe a disease characterized by. Scleroderma is a longterm disease that causes hardening and tightening of your skin and connective tissues. Connective tissues support your skin and surround your organs. Scleroderma is an autoimmune disease. This means your immune system mistakes healthy body tissue for a. Scleroderma Foundation, Danvers, MA. 28, 313 likes 804 talking about this 123 were here. The Scleroderma Foundation is the national organization for Scleroderma is an autoimmune disorder, which means that the body's immune system turns against itself. In scleroderma, there is an overproduction of abnormal collagen (a type of protein fiber present in connective tissue). Scleroderma (skleerohDURmuh) is a group of rare diseases that involve the hardening and tightening of the skin and connective tissues the fibers. Scleroderma, or systemic sclerosis, is a chronic connective tissue disease generally classified as one of the autoimmune rheumatic diseases. If you have scleroderma, you have areas of hardening of the skin. In one type of scleroderma, called systemic sclerosis, you can also get hardening of some of your internal organs. This stops them working normally. Scleroderma (also known as systemic sclerosis) is a chronic disease that causes the skin to become thick and hard, a buildup of scar tissue, and damage to internal organs such as the heart and blood vessels, lungs, stomach and kidneys. Scleroderma is a rare, chronic disease of the immune system, blood vessels and connective tissue. 5 million people worldwide have scleroderma, and in. Scleroderma is a rare, chronic rheumatic disease. The combined forms of scleroderma, including localized, systemic, and related conditions, affect an estimated 300, 000 Americans, primarily females who are 30 to 50 years old at onset. Scleroderma causes thick, hard patches of skin. Symptoms of scleroderma vary a lot, depending on the type of disease you have. There is no cure for scleroderma, but you can reduce damage from the disease with proper treatment. Scleroderma News is strictly a news and information website about the disease. It does not provide medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. This content is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Scleroderma is a rare, autoimmune condition in which the body produces too much collagen, causing the skin and connective tissue to thicken. Scleroderma is a disease of the body's connective tissue. Scleroderma means 'hard skin The most common symptom is a thickening and hardening of the skin, particularly of the hands and face. Scleroderma, or systemic sclerosis, is a disorder of connective tissue of uncertain causation characterized by inflammatory, fibrotic (increase of fibrous tissue), and degenerative changes in the skin, joints, muscles, and certain internal organs. Systemic scleroderma, also called diffuse scleroderma or systemic sclerosis, is an autoimmune disease of the connective tissue. It is characterized by thickening of the skin caused by accumulation of collagen, and by injuries to small arteries. There are two forms of scleroderma: localized and systemic. The localized (nonsystemic) form affects the skin of only the face, hands, and feet. A support community connecting scleroderma patients and caregivers. Get advice and information about new diagnoses, treatments, and more. The Scleroderma Foundation is a national nonprofit health organization dedicated to a threefold mission of Support, Education, and Research to help fight this challenging autoimmune disease. Scleroderma is a chronic but rare autoimmune disease in which normal tissue is replaced with dense, thick fibrous tissue. Although it most often affects the skin, scleroderma also can affect many other parts of the body. Scleroderma is a disease that involves the buildup of scarlike tissue in the skin and elsewhere in the body. It also damages the cells that line the walls of the small arteries. Scleroderma is a chronic skin disease, meaning it doesnt go away. Your doctor can treat your symptoms and help you feel better, though. What Are the Symptoms of Scleroderma? When you have scleroderma, the thing youre most likely to notice first is that the skin on your fingers, arms, legs, hands, feet, or face tightens, gets. Scleroderma is an autoimmune, rheumatic, and chronic disease that affects the body by hardening connective tissue. (Connective tissue is widespread. Scleroderma is an autoimmune disease affecting connective tissue (the tissue that connects joints, muscles, blood vessels and internal organs) in the body. Scleroderma affects about 300, 000 Americans. There's no cure and doctors know very little about the mysterious disease. Now, a new center is making it a mission to find out more..